Guides
Practical guides to help you with your projects.
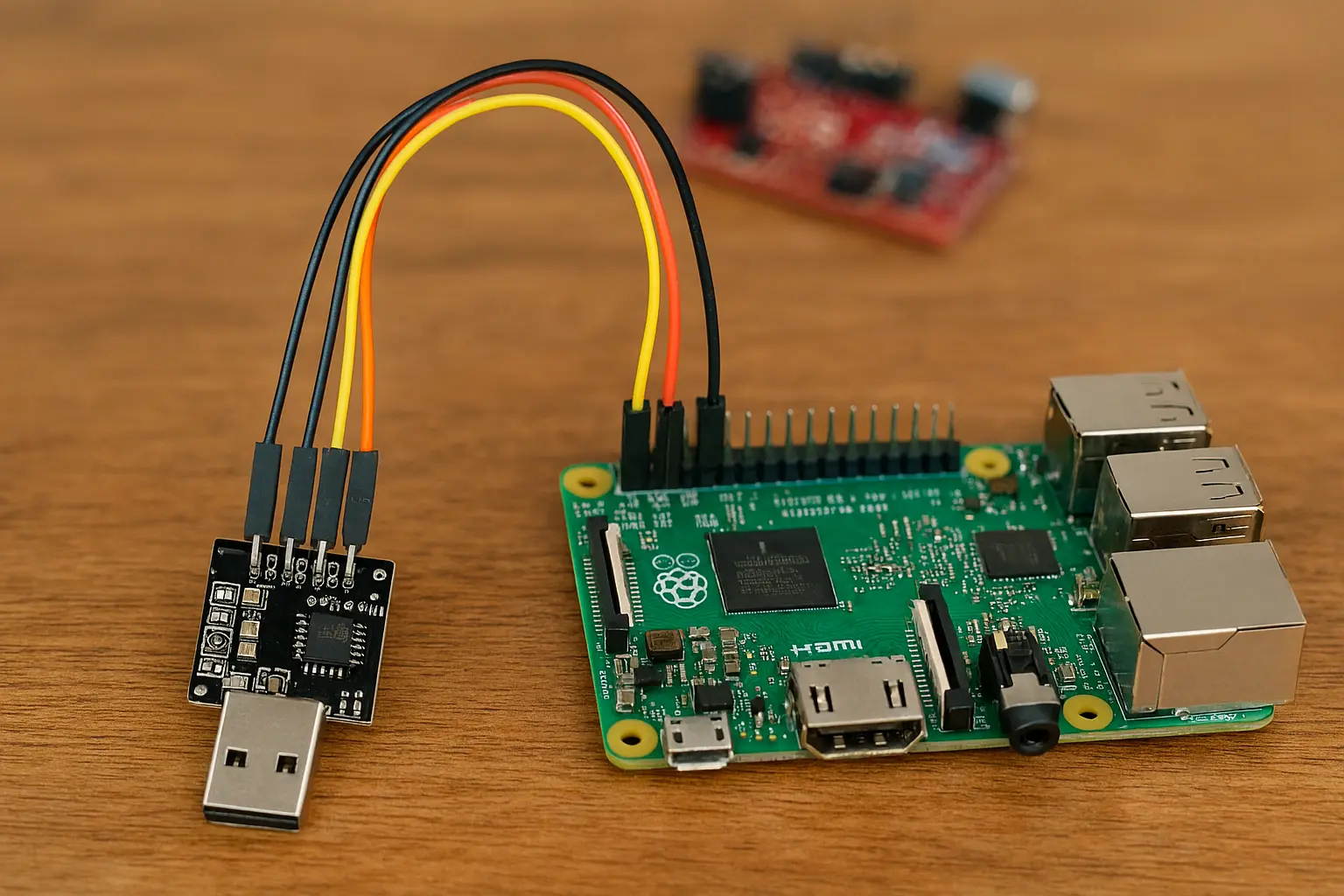
A Raspberry Pi is a full-fledged Linux computer. Most of the time, you interact with it over a network using SSH or by connecting a monitor and keyboard. But what happens when the network is down, or you're setting it up for the first time and don't know its IP address?
The ESP32 is a powerhouse microcontroller, beloved for its built-in Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and dual-core processor. But with great power comes great complexity. When your ESP32 project isn't working—whether it's failing to connect to Wi-Fi or crashing unexpectedly—the serial terminal is your single most important debugging tool.
If you've ever worked with an Arduino, you've probably used its built-in Serial Monitor. It's the simplest way to get feedback from your board. But the serial port is much more than just a debug window—it's a two-way street for communication.
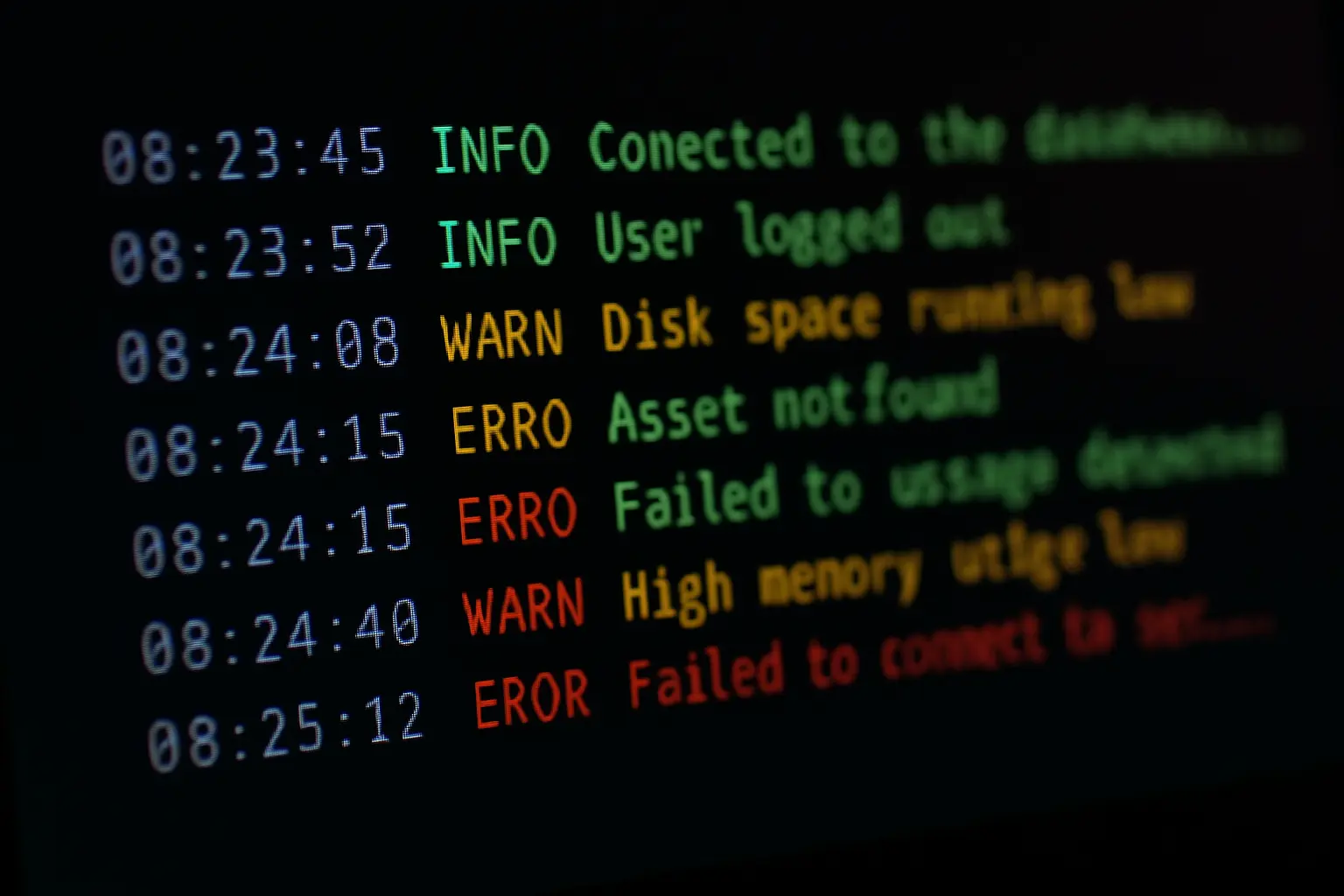
As your projects grow more complex, your serial debug output can turn into a monotonous, hard-to-read wall of text. Did you miss that one critical error message scrolling by? Was that status update a success or a warning?